A subject of conscious activity with a worldview of statuses. Personality as a subject of social life
Mankind is a specific material reality, but as such it does not exist independently. Individuals live and act. The existence of individual representatives of humanity is expressed by the concept of "individual".
Individual- this is a single representative of the human race, a specific carrier of all social and psychological traits of mankind: mind, will, needs, interests, etc. To reflect specifically the historical features of human development at various levels of his individual and historical development, along with the concept of "individual" the concept of "personality" is used.
Word "personality"(Latin persona) originally denoted the mask in which the actor performed in the ancient theater, then it began to denote the actor himself. Later, this word significantly changed its meaning and began to characterize a person in the system public relations where there are already many social roles.
A personality is a human individual who is the subject of consciousness activity, which has a set of socially significant features, properties and qualities that it implements in public life. When talking about a person, first of all, they mean its social individuality, uniqueness.
This is a complex concept that embodies the result of the development of an individual, the most complete embodiment of all human qualities, which can be characterized as follows: a subject of conscious activity, possessing a set of socially significant features, properties and qualities that he implements in public life. When talking about a person, first of all, they mean its social individuality, uniqueness. The latter is formed in the process of upbringing and human activity under the influence of a particular society and its culture. Not every person is a person. Humans are born, they become individuals in the process of socialization.
Obviously, the concept of personality differs from the concept of individuality, which characterizes the originality, uniqueness, originality of a given person. Personality is a concept that shows that certain traits that appear in an individual carrier are socially significant.
The philosophical understanding of personality makes it possible to answer the questions: what place does a person take in the world; who he is; who he can and should become; how the individual potential of a person is realized in his social everyday life; how he plays his social role; what is his measure of responsibility for words and deeds, the measure of freedom; how he controls himself; How does it develop and live?
Personality and individuality.
Previously, the word "individual" had an exclusively biological meaning and denoted a separate "individual" as a representative of a biological species. The further development of this concept led to the fact that its content retained the features of a representative, species, but to a greater extent it began to indicate a separate object with unique qualities, features of biography, character, abilities, appearance, behavior, etc.
The concepts of “personality” and “individual” have gone through a long history in their development and, in enriching their content, reflected the processes that took place in society, as well as in the development of philosophical thought.
These concepts have entered everyday and literary use. Thus, a person is often characterized as strong or weak, bright or colorless, rich or poor (in terms of spiritual components), open or closed, etc.
Taking into account the development of information saturation of social relations, the deployment of various forms of communication, the personality began to be defined as a manifestation of individuality in social communication.
Personality is the embodiment of a certain social character, individual and, at the same time, typical, social. Personality, therefore, can be defined as an individually expressed phenomenon. Thus, only that person can be called a personality who, in his actions, behavior and thinking, is distinguished by independence and self-sufficiency, this is nothing more than an individuality, which is a personality trait.
social role, which the individual performs, is formed and has meaning only in society, in this sense, the individual always expresses himself as a representative of a particular society, historical era, i.e. bears typical features. However, a personality is always unique, since it always realizes the social, typical, in an individual, unique form. In addition, we must not forget that the causes of individually unique features are determined by a set of genes received from parents, and in this sense, each person is unique. This uniqueness is carried out through the signs peculiar only to a given person: features of temperament, character, facial features and, in general, the whole bodily appearance. Therefore, a person is always individual.
1. Until now, there are small tribes that are at the stage of primitive relations and do not have contacts with the rest of the world. They practically do not engage in economic activity, extracting everything necessary for existence from nature. The fruits they collect, the animals they get, become the property of the entire tribe and are distributed according to the equalizing principle by the leader of the tribe. Do these tribes live a natural or social life? Justify your answer (give 2 reasons).
correct answer
The tribes indicated in the text, despite their close connection with nature, live:
social life.
2 reasons for your opinion:
1) people living in a tribe are connected by collectivist (i.e., social) relations;
2) in these tribes there are leaders (i.e., there are power relations and primitive, but public administration).
2. The definition "A subject of conscious activity, having a set of socially significant features, properties and qualities that he implements in public life" refers to the concept:
1. person 3. individuality
2. personality 4. individual
correct answer
2. personality
3. A person, unlike an animal, is capable of:
1. show emotions 3. set goals
2. take care of offspring 4. take action
correct answer
3. to goal setting
4. Human activity and animal behavior is characterized by:
1. self-control mechanism 3. goal setting
2. satisfaction of needs 4. awareness of the choice of means
correct answer
2. Satisfying needs
5. Find in the list below social phenomena, and write down in response the numbers (without commas and spaces) under which they are indicated:
1) animal protection law 3) evolution of fish species 5. education reform
2) photosynthesis 4) revolution 6. volcanic eruption
correct answer
145
6. Find in the list a concept that is general for all the others, and write it out as an answer.
sphere, element, subsystem, structure of society, groups and associations of people, person, individual.
correct answer
structure of society
7. Definition: “The direction of development, which is characterized by the transition from higher and perfect forms and structures of society to lower and imperfect structures”, refers to the concept:
1. evolution 3. revolution
2. reform 4. regress
correct answer
4. regression
8. Find a concept in the list that is general for all the others, and write it out as an answer.
motherhood, family institution, childhood, fatherhood, socialization, marriage institution.
correct answer
family institution
Material for preparation:
deyavalidity – ak shape human activity, directed on transforming them aroundworld (in reality or through consciousness).
Structure- the structure (device, composition) of something or someone.
Structure (structure) any activesti:
motive(motivating reason for activity);
1. subject (the one who carries out the activity: an individual or a group of individuals, an organization, etc.);
2. object(something or what or who, for which the given figuredirection);
3. purpose (formation in the mind of the subject of activityideal image of that result,which a person seeks to achieve as a result of activity);
4. fundsits (goal) is achieved nia (after targetingthe individual decides what will help him, with what help he can (i.e., what meanshe needs to use) to achieve the goal);
5. result(real image obtained by the subject as a result of activity).
E if the goal is clearly set, the means are chosen correctly,then the outcome of the activity will becoincidence of the ideal image of the result with the real one, i.e. it makes sense to say that the goal of the activity has been achieved by the subject.
Depending on the received the result of the activity canbe characterized:
- destructive;
- creative.
The main motive, I encourage schy person to activity: desire to satisfyyour needs ( physiologically e; social; ideal).
Known in one way or anotherpeople, needs become paramount source of their activity.
important role in activities (in addition to needs) is played by beliefs of peopleregarding the goals ryh to be reached, os new ways and means leading to the achievement of goals.
Belief - an opinion firmly established in a person, a confident look at something or someone, a point of view.
Sometimes in the choice of ways and meanspeople are guided byliving in a stereotypical societymi, i.e., some common, y grown ideas aboutanything, and sometimes go against stereotypes.
Stereotype – a pattern (model) of thinking or behavior that has been established in society.
The activity has a hugeinfluence on the personality, being the basis on which personality development takes place. In pro activity of an individual moralizes and asserts itself as a person, it is the process activities underpinsocialization of the individual. OkazyWai converting influenceimpact on the environment, lovek not only adapts (adapts) to the natural and social environment, but rebuilds and improves her.
The whole history of human societies - the history of human activities.
Socialization of the individual. Interpersonal relationships
Personality is a human individual who is the subject of conscious activity, possessing a set of socially significant features, properties and qualities that he implements in public life. When talking about a person, first of all, they mean its social individuality, uniqueness. The latter is formed in the process of upbringing and human activity, under the influence of a particular society and its culture. Not every person is a person.
Humans are born, they become individuals in the process of socialization.
Socialization n is called ongoing throughout the life of individuals the process of influence of society and its structures on them, as a result of which people accumulate social experience of life in a particular society, become individuals. Socialization should be distinguished from adaptation (a time-limited process of getting used to new conditions of existence), learning (the process of acquiring new knowledge about the world around an individual), maturation (the sociopsychological development of a person in a narrow age range from 10 to 20 years).
Socialization begins in childhood, continues through adolescence and into adulthood. Its success depends on how much a person, having learned the values and norms of behavior accepted in a given culture, will be able to realize himself in the process of social life. The environment surrounding a person can influence the development of a person both purposefully (by organizing training and education) and unintentionally.
The process of socialization goes through several stages, which sociologists call life cycles: childhood, youth, maturity and old age. Life cycles are associated with changing social roles, acquiring a new status, changing habits and lifestyles. According to the degree of achievement of the result, they distinguish between initial, or early, socialization, covering the periods of childhood and adolescence, and continued, or mature, socialization, covering maturity and old age.
The formation of a person's personality in the process of socialization occurs with the help of so-called agents and institutions of socialization.
Socialization agents are defined as specific people responsible for teaching other people about cultural norms and helping them master various social roles. Distinguish agents of primary socialization(parents, brothers, sisters, close and distant relatives, friends, teachers, etc.) and agents of secondary socialization(officials of the university, enterprises, television employees, etc.). Agents of primary socialization constitute the immediate environment of a person and play an important role in the process of forming his personality, agents of secondary socialization have a less important influence.
Institutes of socialization - these are social institutions that influence the process of socialization and guide it . Like agents, socialization institutions are also divided into primary and secondary. An example of a primary institution of socialization can serve as a family, school, secondary - means mass media, army, church.
The primary socialization of the individual is carried out in the sphere of interpersonal relations, the secondary - in the sphere of social relations.
Agents and institutions of socialization perform two main functions:
1) teach people accepted in society cultural norms and patterns of behavior;
2) carry out social control over how firmly, deeply and correctly these norms and patterns of behavior are assimilated by the individual.
Therefore, such elements of social control as encouragement (for example, in the form of positive assessments) and punishment (in the form of negative assessments) are at the same time methods of socialization.
During the period of secondary socialization, a person can be the subject of the processes of desocialization and resocialization.
Desocialization represents a loss or conscious rejection of learned values, norms of behavior, social roles, habitual way of life. Resocialization called the opposite process of restoring lost values and social roles, retraining, the return of the individual to a normal (old) way of life. If the process of desocialization is negative and deep enough, it can destroy the foundations of the personality, which will be impossible to restore even with the help of positive resocialization.
All interpersonal relationships are subdivided into official and unofficial.
Official and informal interpersonal relations differ from each other, firstly, by the presence or absence of a certain normativity in them. Official relations are always regulated by some specific norms - legal, corporate, etc. Secondly, official relations are standardized and impersonal, that is, the rights and obligations that develop within official interpersonal relations do not depend on the individual, while how informal interpersonal relationships are determined by the individual personal characteristics of their participants, their feelings and preferences. Finally, in official relations the possibility of choosing a communication partner is extremely limited, while in informal relations it is the choice of the individual that plays the decisive role. Such a choice is made by communication partners, depending on the inherent needs of each of them for communication and mutual
action with a person who is quite definite in his personal qualities.
The formal and informal interpersonal relationships that people enter into with each other are extremely diverse. They can be short-term (fellow travelers on the train), long-term (friends, colleagues), permanent (parents and their children), causal (criminal and victim), functional (customer and tailor), educational (teacher and student), subordinate (boss and subordinate).
Choose one correct answer from those given. Enter your answer in the table.
Task 1.1
Which of the following situations leads to a decrease in demand for a product or service?
- rise in price of substitute goods
- reduction in the number of consumers
- active advertising in the media
- improving the quality of a product or service
Task 1.2
The process of familiarization with the culture, values of human society, knowledge of the world, accumulated by previous generations, is called
- the science
- art
- education
- creation
Task 1.3
The properties and roles of a person, which he acquires only in interaction with other people, characterize him as
- individual
- individuality
- organism
- personality
Task 1.4
Which of the following statements characterizes world religions?
- importance of ancestor worship
- animal sacrifice
- formal equality of all people in the face of higher powers
- use of magical practices
Answer :
| 1.1. | 1.2. | 1.3. | 1.4. |
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 3 |
Evaluation criteria
By 1 point for each correct answer.
Maximum per task 4 points.
Task 2
Choose multiple correct answers. Enter your answers in the table.
Task 2.1
Choose from the list below the principles laid down in the Constitution of the Russian Federation:
- dominance of state property
- principle of democracy
- giving women more rights than men
- welfare state principle
- local government guarantees
Task 2.2
Which of the following is property income?
- deposit interest
- winning the lottery
- rent
- wage
- dividends
Task 2.3
Choose from the list below the civil (personal) rights and freedoms of a person.
- right to privacy
- right to a healthy environment
- the right to freedom of movement and choice of residence
- the right to protection of honor and dignity
- the right to participate in the administration of state affairs
Answer :
| 2.1. | 2.2. | 2.3. |
| 245 | 135 | 134 |
Evaluation criteria
2 points for the correct answer. 1 point for an answer with one error (one of the correct answers is not indicated or one incorrect answer is given along with all the correct answers).
Maximum per task 6 points.
Task 3
What unites the following concepts? Give the most accurate answer.
Task 3.1
Legal custom, legal precedent, legal act.
Answer: sources of law.
Task 3.2
Nutrition, contacts with others, recognition of personal achievements, security.
Answer: human needs.
By 3 points for each correct answer.
Maximum per task 6 points.
Task 4
Give a brief rationale for the series (what unites the listed elements). nIndicate which of the elements is superfluous on this basis.
Task 4.1
Italy, Russia, France, Netherlands, Poland, Hungary.
Answer: republics. Excess - the Netherlands.
Task 4.2
Withdrawal, compromise, mobility, mediation.
Answer: ways to resolve the conflict. More than that, mobility.
Evaluation criteria
By 4 points for each correct answer 2 points for the right reason 2 points for pointing out the excess).
Maximum per task 8 points.
Task 5
"Yes or no"? If you agree with the statement, write “yes”, if you disagree, write “no”. Record your answers in the table.
Task 5.1.
The maternity capital program is one of the ways to solve the demographic problem in the Russian Federation.
Task 5.2.
The description and procedure for the official use of state symbols of the Russian Federation is established by the Constitution of the Russian Federation.
Task 5.3.
Rituals serve to maintain the integrity of the human collective.
Task 5.4.
AT modern society the level of education does not affect belonging to one or another stratum.
Task 5.5.
Inheritance matters are governed by civil law.
Answer :
| 5.1. | 5.2. | 5.3. | 5.4. | 5.5. |
| Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes |
Evaluation criteria
By 2 points for each correct position.
Maximum per task 10 points.
Task 6
Fill in the scheme, indicating the category common to all images (generalizing concept), as well as its constituent elements. Enter in the appropriate cells the letter designations of the illustrations that relate to the elements you named.

Figure A

Figure B

Figure B

Figure D
Answer :
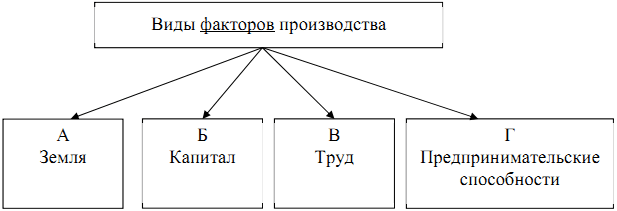
2 points for pointing out the general concept. By 2 points for each completely correct filling of the cells of the second level of the scheme.
Maximum per task 10 points.
Task 7
Solve a logical problem.
Three friends met - Serova, Krasnova and Chernova, dressed in gray, red and black dresses. The girl in gray said to Chernova: "Let's change dresses so that their color matches the names!" What color dress was on each of the girlfriends originally?
Answer : Krasnova - a gray dress, Chernova - a red dress, Serova - a black dress.
reasoning : If a girl in gray turned to Chernova with her proposal, then her friend was wearing a red dress (not black, because the dresses did not initially correspond to the surnames). Therefore, the girl in gray is Krasnova. Thus, Serova initially wore a black dress.
Evaluation criteria
3 points for answer. 4 points for a complete discussion. If one of the stages of reasoning is omitted - 1 point. If more - 0 points.
Maximum per task 7 points.
Task 8
Establish a correspondence between the forms of government and specific historical examples: for each position given in the first column, select the corresponding position from the second column. Enter your answers in the table.
| FORM OF GOVERNMENT | EXAMPLE OF GOVERNMENT |
| 1) federation 2) confederation 3) unitary |
A) An important milestone in the history of Switzerland was the agreement concluded in 1291 by the three cantons on joint defense in the event of an attack by the Holy Roman Empire. B) There are 85 equal subjects in Russia, including 22 republics, 9 territories, 46 regions, 3 federal cities, 1 autonomous region, 4 autonomous districts. C) It was this form of government that existed in the first 13 colonies in North America, united to fight Great Britain. D) Art. 3 of the Constitution of the Republic of Poland of 1997 defines Poland as a single state. |
Answer :
| BUT | B | AT | G |
| 2 | 1 | 1 | 3 |
Evaluation criteria
By 1 point y for each correct position.
Maximum per task 4 points.
Task 9
Insert instead of gaps the serial numbers of the corresponding words from the proposed list. Words are given in the list in the singular, adjectives in the masculine form. Pay attention: in the list of words there are those that should not occur in the text! Enter your answer in the table.
The most important condition for social ______ (A) and effective ______ (B) of the social system is ________ (C) social actions and social behavior of people, in the absence of which the social system is waiting for ________ (D) and collapse. Society has certain means by which it provides _________ (D) of existing social relations and interactions. One of these means is social ___________(E), the main function of which is to create conditions for the stability of the social system, the preservation of social __________(F) and at the same time for positive social changes. This requires flexibility from social control, including the ability to recognize positive-constructive __________(S) from social norms that should be encouraged, and negative-dysfunctional deviations, to which certain ________(S) (from Latin sanctio - the strictest ruling) should be applied. ) negative character, including ________(K).
List of terms :
- stability
- sustainability
- interaction
- deviations
- administrative
- justification
- monitoring
- sanctions
- predictability
- reproduction
- control
- violent
- functioning
- civil
- legal
- subordination
- disorganization
- criminal
- situation
Answer :
| BUT | B | AT | G | D | E | AND | W | And | To |
| 3 | 13 | 9 | 17 | 10 | 11 | 1 | 4 | 8 | 15 |
Evaluation criteria
By 1 point y for each correct insertion.
Maximum per task 10 points.
Task 10
Read the text carefully and answer the questions.
Social norms are those basic forms and means by which the regulation of behavior and social relations of people is carried out. They express in a concentrated form the objective need of any society to streamline the actions and relationships of its members, to subordinate their behavior socially. necessary rules. Thereby social norms act as a powerful factor in the conscious and purposeful impact of the social community on the image, method and forms of people's life ...
Law has played an important role in the system of social regulation since its inception. For all its relative independence, law, like other types of social norms, performs its specific regulatory functions not in isolation and apart, but in a single complex and in close interaction with other social regulators...
A special type of social norms are corporate norms, i.e. norms adopted by public associations and regulating relations between their members or participants ...
Fixed in the documents of a public association (political
party, trade union, body of public amateur performance, etc.) the norms apply only to members and participants of this public association and are binding only on them. Violation of these corporate norms entails the application of appropriate sanctions provided for by the charter of the organization.
Corporate norms (in terms of their regulatory significance, scope, range of addressees, etc.) are group norms of an intraorganizational nature ... At its core, corporate norms are not a product of lawmaking by public associations themselves, but only a form and method of using and exercising constitutional rights citizens to associate, and the creation and activities of public associations, including their rule-making, must be carried out on the basis and within the framework of the law, in accordance with the universal requirements of law and the legal form of public relations (observance of the principle of legal equality, voluntariness, the relationship of rights and obligations, etc.). e.) ...
(V.S. Nersesyants)
- Who, according to the author, is subject to corporate regulations? Which document contains sanctions for violation of corporate norms?
- Name two types of norms that are not named by the author. Give examples of these norms.
- What needs of society, according to the author, express social norms? List two needs. Give an example illustrating the implementation of one of the two needs you named.
- Using the text, name the difference between corporate norms and legal norms. Explain how the dependence of corporate norms on the rule of law is manifested.
Answer :
1. a.“The norms enshrined in the documents of a public association (political party, trade union, body of public amateur performance, etc.) apply only to members and participants of this public association and are obligatory only for them.
b. Violation of these corporate norms entails the application of appropriate sanctions provided for by the charter of the organization. Formulation can be arbitrary. By 2 points for every answer. Total 4 points.
2. Custom, religious norms, morality. Other types of rules may be given. For each named norm 2 points. Total 4 points.
The following examples can be given: the custom of decorating a Christmas tree on New Year. Religious norms - fasting before major religious holidays. Moral - don't lie, don't steal. . By 2 points for each example. Total 4 points. Maximum 8 points.
3. 1) In streamlining the actions and relationships of its members; 2) in subordinating the behavior of members of society to socially necessary rules. By 2 points for each named need. Total 4 points. The following examples can be given: the rules of the road regulate the behavior of its participants and ensure their safety; the student at school learns to fulfill the requirements. Other examples can be given. 3 points for the correct example. Maximum 7 points.
4. 1) Rules of law are established by the state, and corporate norms - by one or another public association; 2) the creation of corporate norms should be carried out on the basis and within the framework of the law, in accordance with the universal requirements of law and the legal form of public relations.
By 3 points for the correct answer to each question. Total 6 points.
Maximum per task 25 points.
Task 11
Solve the social science crossword puzzle.
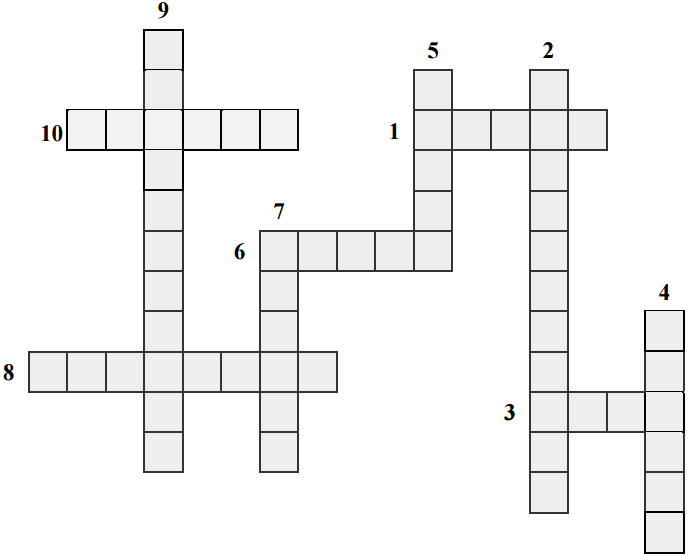
Horizontally:
- 1. The totality of all relations, as well as forms and organizations of cooperation between people with each other, relating to the sale of goods and services.
- 3. The activity of people in the production of economic goods.
- 6. Malaya social group, united by blood relationship, marriage ties, raising children, living together.
- 8. The subject of conscious social activity, having a worldview, statuses, roles, who has undergone socialization.
- 10. Direct exchange of one product for another product.
Vertically:
- 2. The system of political institutions involved in the organization of public life in a certain territory.
- 4. Consolidated legislative act, which combines the norms related to one branch of law.
- 5. The armed forces of the country, performing the function of any state to protect its territory, borders and population.
- 7. A certain position in the social structure of groups or society, associated with other positions through a system of rights and obligations.
- 9. Purposeful training of the individual, the formation of certain knowledge and skills.
Answer :
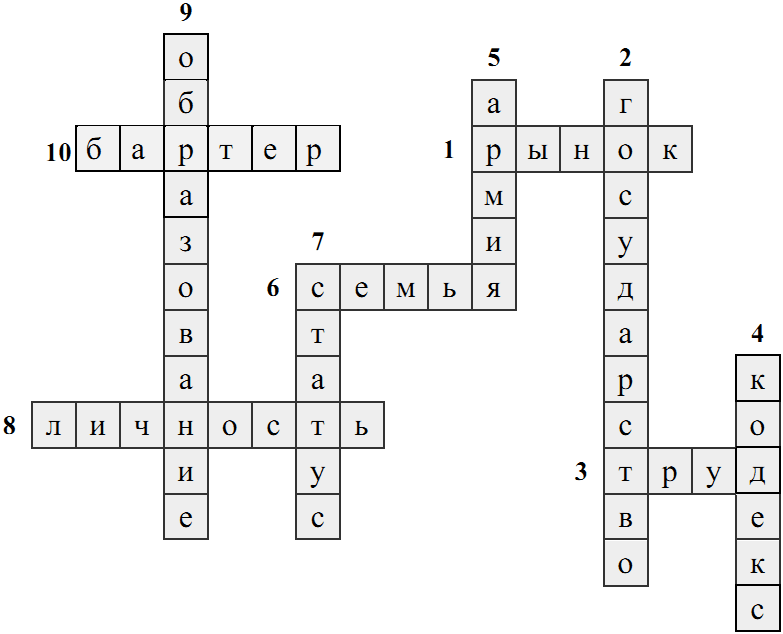
1 point for each correct position.
Max per task 10 points.
Max per job 100 points.